

How Flint and SchoolAI compare in ease of use, implementation, safety, and transparency
TOP SCHOOLS USE FLINT TO OFFER SAFE AI ACCESS TO STUDENTS, TEACHERS, AND ADMINISTRATORS
Introduction
At face value, SchoolAI and Flint may appear pretty similar: both are AI platforms built for K-12 students and districts, promote personalized learning, and offer teacher and student tools. However, their functionality, impact, and transparency could not be more different. Despite its offerings, SchoolAI is hard to navigate, unable to support knowledge with credible sources, and ultimately limits student engagement, curiosity, and learning.
We’ll be covering the key differences between Flint and SchoolAI, mainly covering:
Teacher ease of use
Interactive student functionality
Student usage experience
Data privacy and security
AI Transparency
From interactive activity generation to multi-layered data protection and in-line citations, Flint empowers students and teachers to use AI for creative, interactive learning. It’s why hundreds of thousands of teachers and students use Flint for personalized learning, not just AI automation.
Key differences between Flint and SchoolAI
Teacher ease of use


Teacher tools and activity builders are available on both Flint and SchoolAI. However, they differ significantly in their application and ease of use.
With Flint, teachers can choose to create activities using a chat-based interface that lets them easily adjust content with AI. Flint can also retain context from earlier messages, meaning that teachers can request edits and modifications based on the original prompt without having to start from scratch.
Flint can also automatically generate suggestions based on a teacher’s suggestions, requests, and edits. It’s like having a normal conversation with an ideal teaching assistant.
Meanwhile, SchoolAI requires teachers to write prompts and do prompt engineering. Since each prompt is treated independently and there is no memory, teachers face the time-consuming task of fine tuning instructions, seeing a preview, and manually rewriting and adjusting the prompt if it does not show the intended results. Flint also has this manual build option if preferred.
Flint also offers templates offers activities pre-built by teachers and can be filtered by subject. Meanwhile, SchoolAI’s dashboard interface can feel overwhelming, making it difficult for teachers to find what they are looking for.
Interactive student functionality


AI education platforms should help foster and accelerate student curiosity. With Flint, students are able to have an interactive AI experience, exploring subjects like Algebra and Biology using an AI-powered whiteboard where they can draw, write text, and upload images.
Students can draw parabolas, show step-by-step how they got to their solution, and get real time feedback with AI vision support and analysis. Flint can even create graphs and charts using a built-in graphing calculator, making key math concepts turn into visual, interactive activities.
Flint’s interactive capabilities extend beyond STEM. Students can have real-time conversations with Flint in over 50 languages, learning essential vocabulary and conjugation using voice chat. Teachers can also listen to these conversations to hear their students’ pronunciation, a crucial feature for language learning that cannot be found on SchoolAI’s platform.
Some of Flint's additional features include:
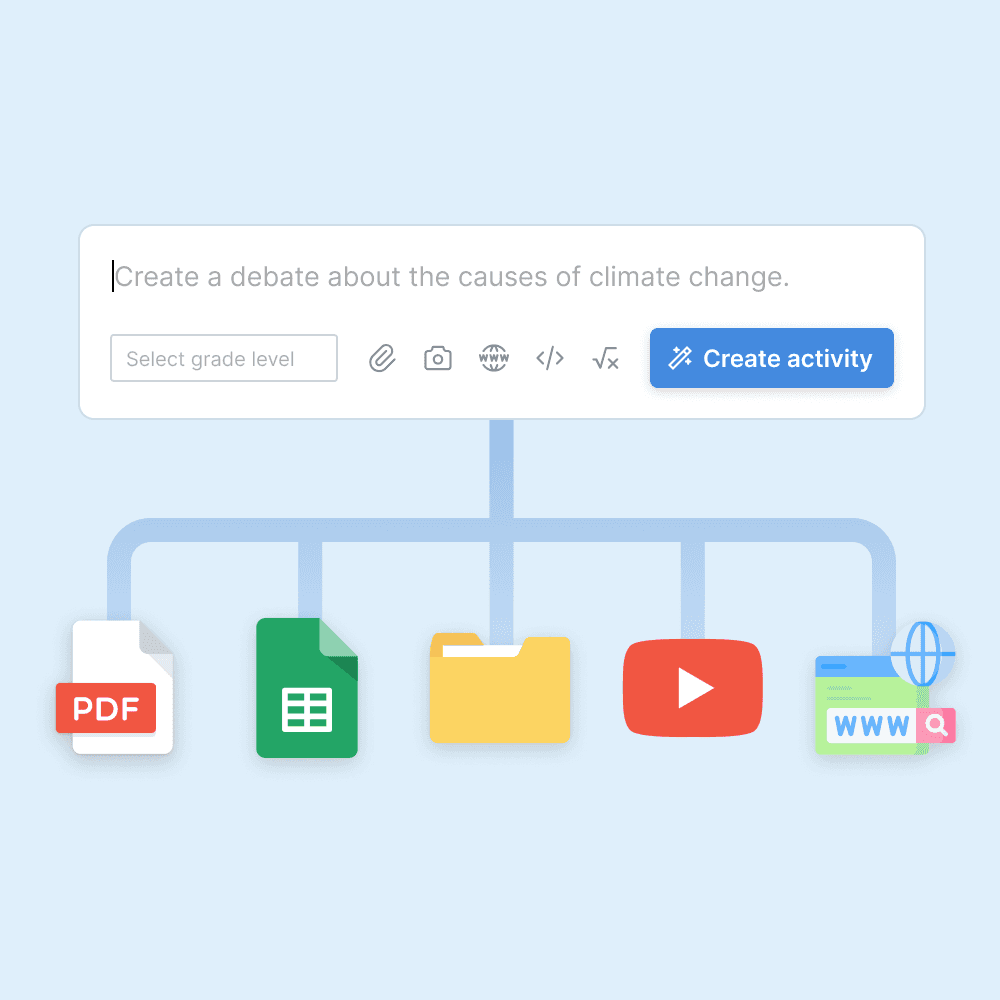
Content upload
Upload PDFs, Word documents, PowerPoint slides, CSV files, and website links for the AI to pull from.
1
of 31

Math accuracy
Flint runs calculations in the background to ensure accuracy on even the most complex math problems, similar to a human tutor verifying work with a calculator.
2
of 31

Web search
Flint can search the web to find accurate and up-to-date info (e.g. current events from news articles).
3
of 31
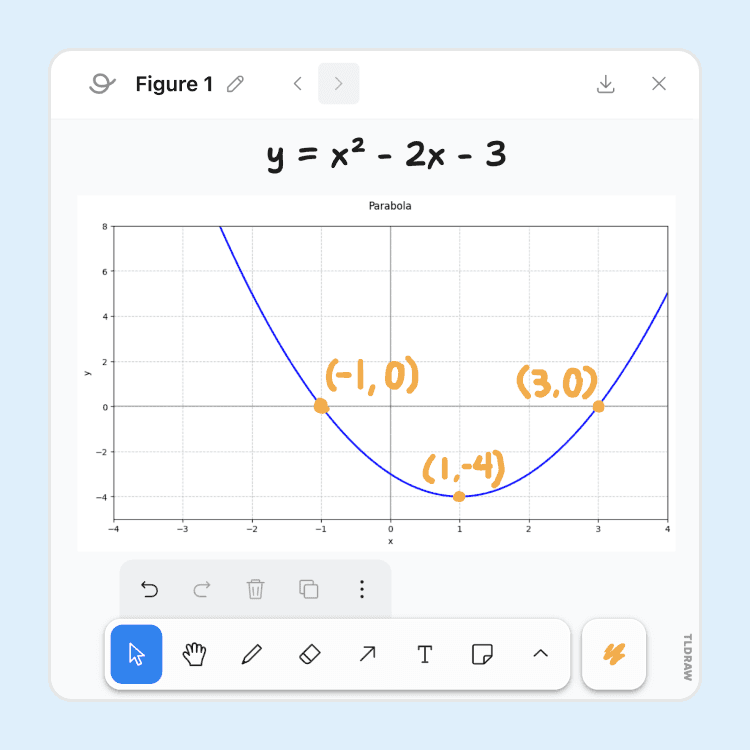
Whiteboard
Students can interact with Flint via a whiteboard to show their work to the AI.
4
of 31

In-line citations
Flint can cite its sources — whether it be from teacher-provided content or web sources the AI found via search — and show the exact excerpt used.
5
of 31

Image processing
Flint can process images to explain diagrams, transcribe written notes, or help students stuck on showing their work on a problem.
6
of 31

Image generation
Flint uses DALL·E 3 to generate AI images to help students visualize scenarios, get inspiration, or create designs.
7
of 31

Evidence-based feedback
When providing feedback after a session, clickable inline citations let students (and teachers) easily identify identify areas of improvement.
8
of 31

Text-to-speech and speech-to-text
Flint can speak in over 50 languages and dialects, and can transcribe speech with 98.5% accuracy.
9
of 31

50+ world languages
World language teachers can select a primary and secondary language for the AI to communicate with students in, as well as a ACTFL or CEFR level.
10
of 31

Code editor
Flint can write and display code in-line in 50+ languages, and includes a built-in code editor with automatic syntax highlighting.
11
of 31

Math formula editor
Flint displays equations in LaTeX formatting and includes a formula editor to let users enter their own equations, in an interface similar to MathType.
12
of 31

Graphing support
Flint can graph equations on 2D or 3D planes to visualize math problems, or help in visualizing simple datasets.
13
of 31

Essay writing feedback
Provide students with inline writing feedback from AI that follows a rubric and guardrails set by the teacher.
14
of 31
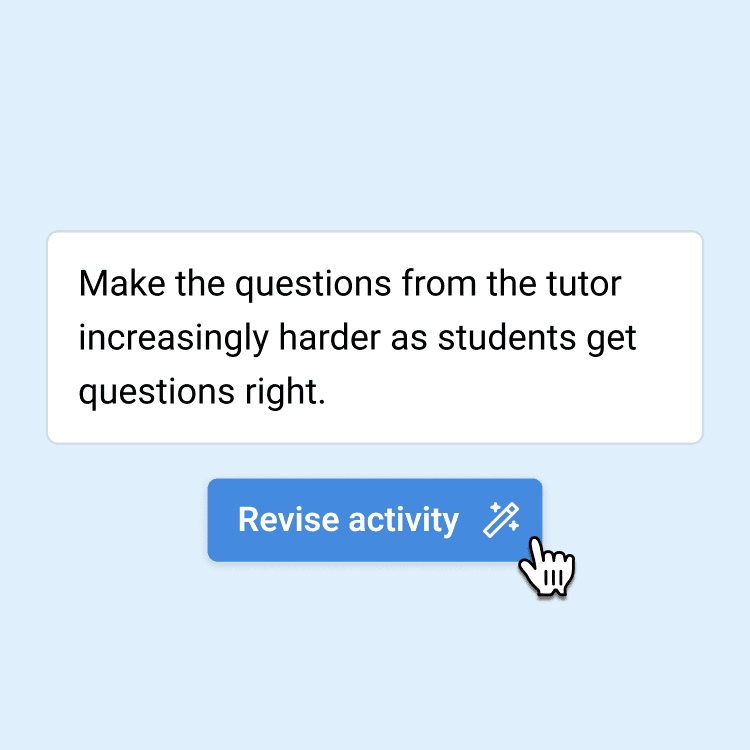
Automatic prompt engineering
Describe what you want in natural language, and let AI do the prompt engineering for you. No prompt engineering skills required.
15
of 31
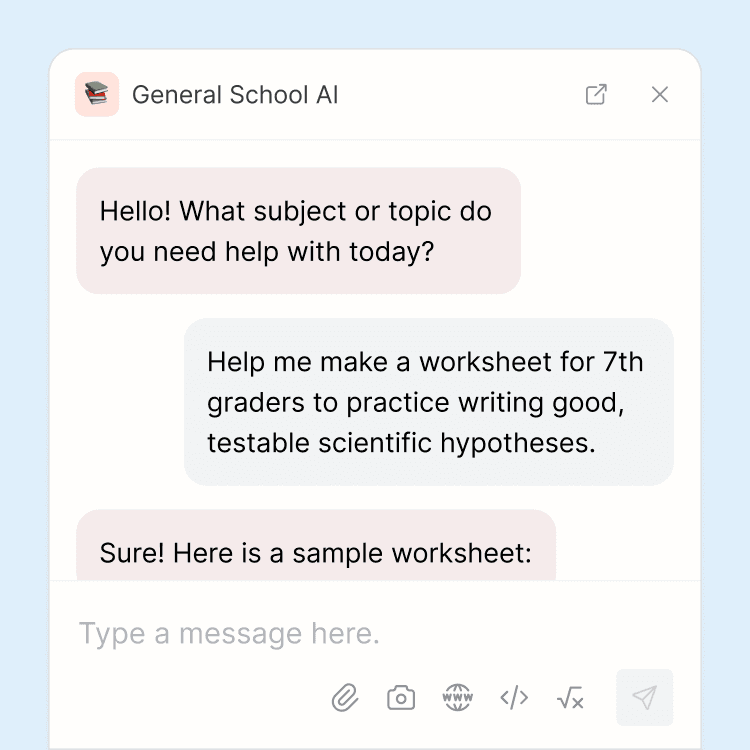
School-wide AI chatbot
Students, teachers, and administrators have 24/7 access to a school-wide AI chatbot that can be used for any purpose, such as extra homework help or for generating classroom materials.
16
of 31

Custom rubrics
Upload rubrics (AP, IB, etc.) for the AI to follow when providing feedback to students, or edit the generated rubric to your liking.
17
of 31

Automated previews
Watch the AI mock up an example student interaction, to see exactly how it would help a struggling student or push an excelling student to go further.
18
of 31
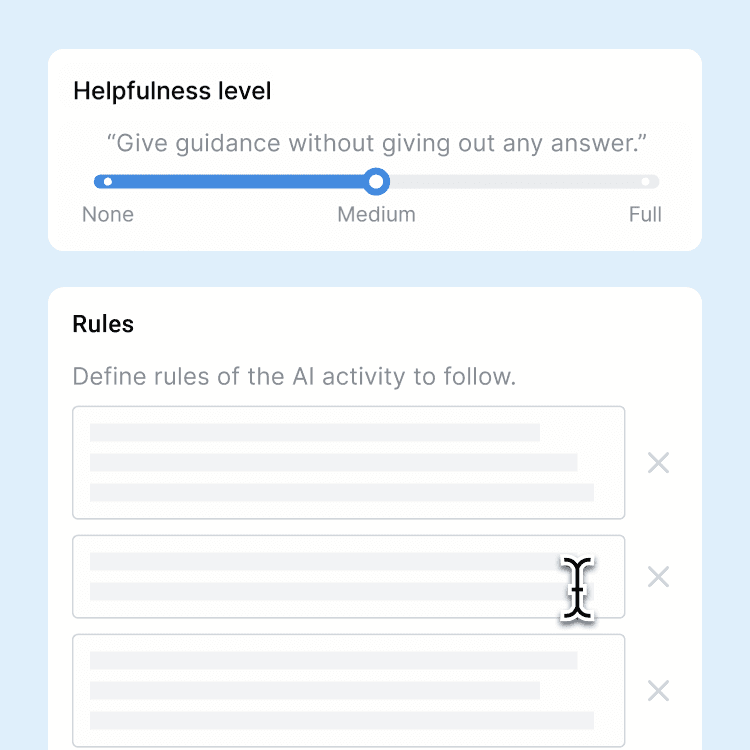
Custom AI guardrails
By default, Flint refuses to provide answers directly or do work on behalf of students. Teachers can customize guardrails the AI follows to make it more or less flexible.
19
of 31
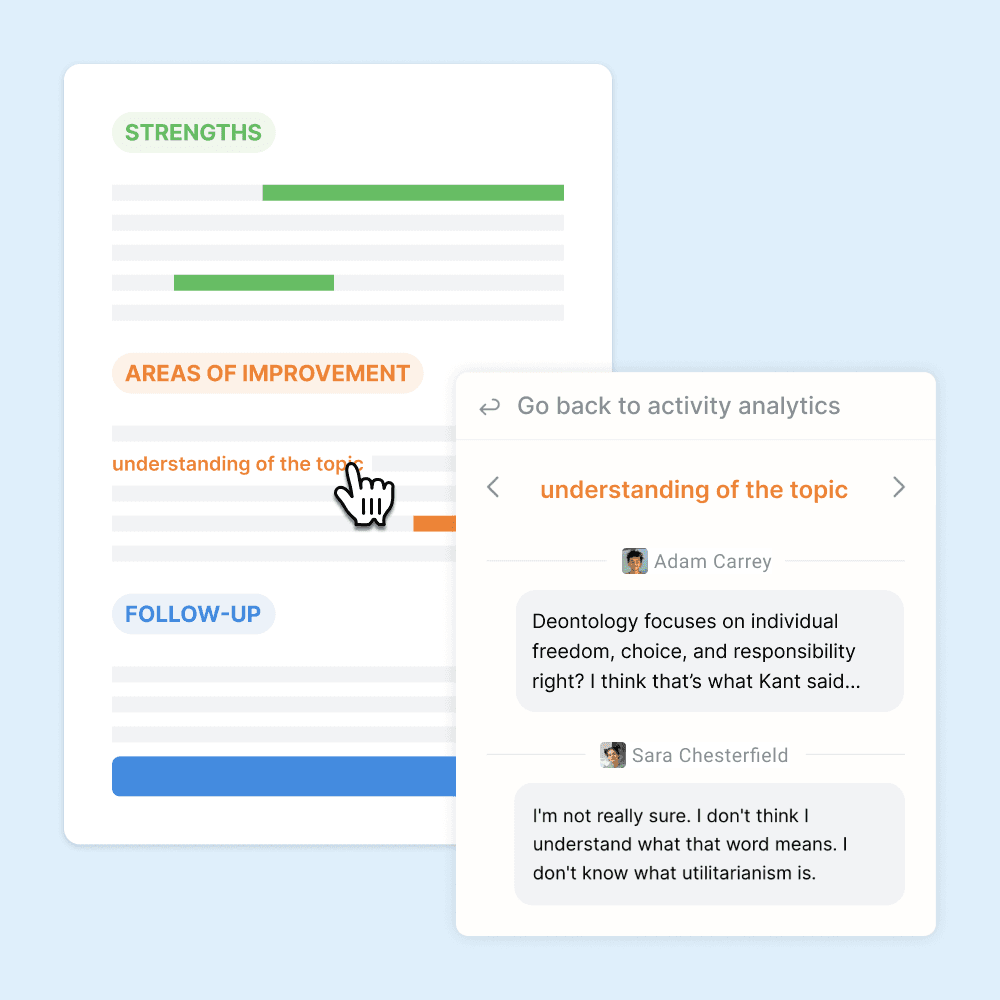
Class-wide summaries
The AI summarizes strengths and areas of improvement for your whole class.
20
of 31

Assignment deadlines
Set a deadline for students to interact with an AI activity, in order to use Flint as an assignment tool.
21
of 31

Timed assignments
Set a time limit for a session with an AI activity.
22
of 31

Follow-up AI activities
Based on areas of improvement of an individual student or an entire class, create an AI activity to give personalized extra help.
23
of 31

YouTube video support
Paste a YouTube video link, and Flint can incorporate the transcript as part of its knowledge base.
24
of 31

Print sessions
Print student conversations with the AI, or export as a PDF.
25
of 31

LMS and SIS integrations
Flint supports rostering import via integrations with every major LMS (Canvas, Schoology, Google Classroom, etc.) and SIS (Veracross, Blackbaud, PowerSchool, etc.)
26
of 31

Automatic flagging
Inappropriate messages sent to the AI (language related to violence, harassment, threats, self-harm, sexual content, etc.) are automatically flagged for administrator review.
27
of 31
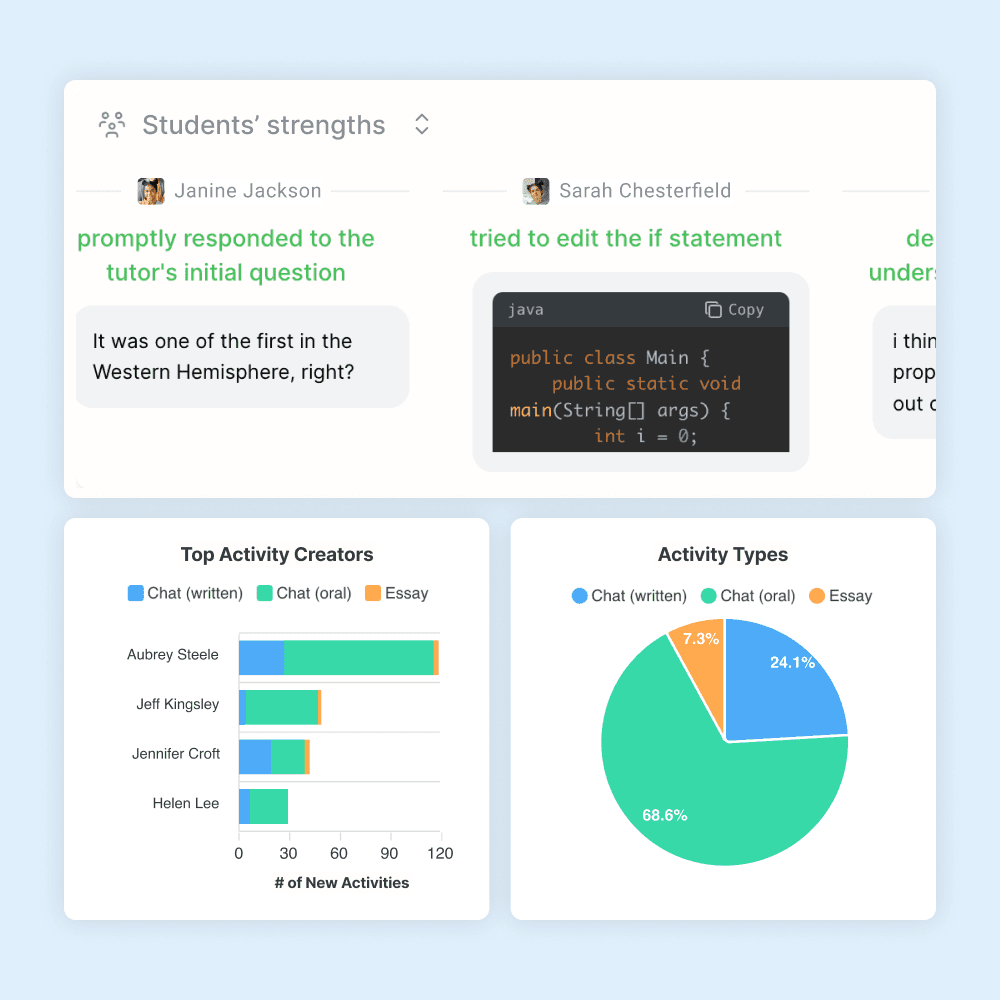
Usage analytics
See how often teachers and students are using Flint, and who the most active users are.
28
of 31

Google and Microsoft SSO
One click sign up via Google or Microsoft, including for students under the age of 13.
29
of 31

Full admin visibility
School admins can see every message that any users (students, teachers, etc.) send back and forth with AI activities on Flint.
30
of 31
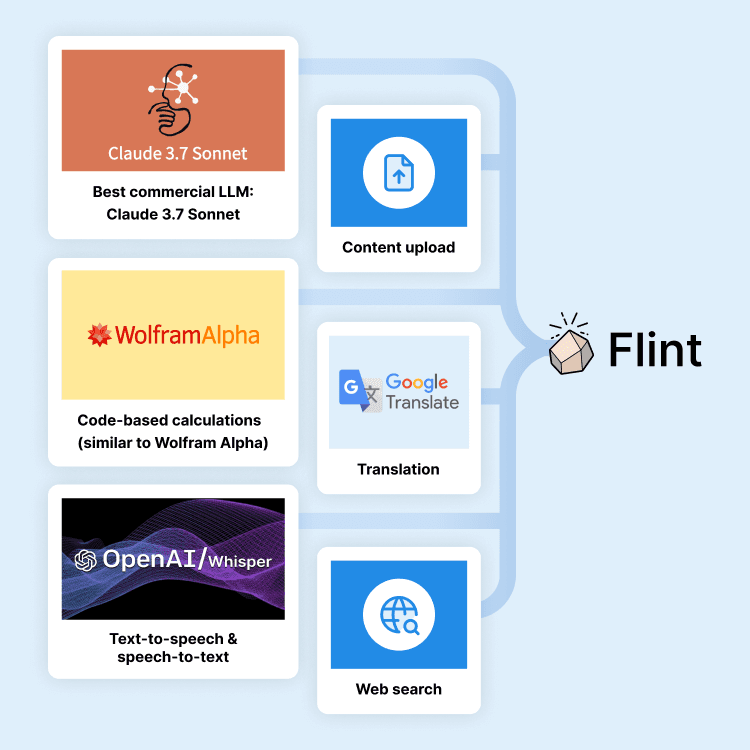
State-of-the-art LLMs
Flint uses Claude 3.7 Sonnet in combination with translation, code-based math calculations, and web search for the highest possible accuracy.
31
of 31
This is not to say that SchoolAI has zero student-facing functionality. However, student interaction is incredibly limited, lacking features comparable to Flint’s whiteboard and code editor. And while you can create STEM-focused student activities with SchoolAI, it is with the major caveat that students are also unable to draw graphs, let alone input basic math functions.
Student usage


Students using Flint also have the ability to learn on their own time, using tools like Flint’s AI Writing Assistant to receive essay feedback, AI Study Guide Maker to print and share study guides, or AI Tutor to supplement their learning. Permitting students to use Flint not only gives them additional support but also allows teachers to look through student interactions with AI outside of assignments and activities, promoting AI safety and transparency.
SchoolAI, on the other hand, does not have student-facing tools, making AI activity creation one-sided. Consequently, students may not be using AI to its full advantage and are unable to be as proactive about boosting their learning with AI tools.
Transparency in AI responses


As AI detectors and plagiarism continue to raise concerns, promoting AI transparency and source validation is crucial to proper AI usage and safety. Flint’s AI responses can be limited to verified sources. Flint can also be designed to cite sources as it gives students information.
Moreover, teachers are able to provide the AI with their own class content, including worksheets, textbook chapters, excerpts, slides, lesson plans, or online sources. These measures significantly cut down issues like hallucination.
AI transparency can be seen in day-to-day interactions with Flint:
Flint is thinking: Platforms like SchoolAI have zero visibility into how they are retrieving information. Flint will pause and say “Let me use a calculator,” “Let me search the internet,” or even just “Let me think,” promoting transparency in how responses are generated.
Math accuracy verification: AI-generated math is often unreliable, making platforms like SchoolAI vulnerable to incorrect solutions. Flint runs calculations using a tool similar to Wolfram Alpha to ensure accurate problem-solving.
Real-time web searches: SchoolAI has knowledge from pre-trained data (as of today, it is trained on knowledge as recent as October 2023). Flint can search the web on the spot and retrieve current, factual information.
In-line source citations: AI responses in Flint include in-line citations so students can see exactly where the information is from, whether that’s teacher-provided materials or external websites sources by the AI. Students can also click the link to visit the original source. SchoolAI cannot provide citations, lacking transparency and not assisting students with further research.
Overall, Flint has holistic approaches to AI transparency that teachers and students cannot find on SchoolAI. If you’re interested in learning more about Flint, you can start for free.
For more info, you can look through our free PD materials, go through our features, see our case studies and use cases, or book a demo to see how you can use Flint in your classroom. You can also check out our Flint vs ChatGPT and Flint vs Magicschool pages to how other AI education tools compare.
Frequently asked questions about Flint and SchoolAI
What is the main difference between Flint and SchoolAI?
Flint is a secure, easy-to-use, transparent AI platform that has a breadth of tools to create personalized, engaging material based on teacher-approved materials or verified sources. SchoolAI offers similar tools but lacks some student features—such as Flint’s Whiteboard—and cannot say where it gets its information, consequently lacking credibility and interactive functionality. Flint empowers teachers and students with safe and AI-assisted learning, making it a more powerful tool for the classroom.
What AI model does Flint use?
Flint is powered by Claude 3.7 Sonnet. Additionally, Flint has custom tooling under the hood — namely text-to-speech, speech-to-text, and a calculator similar to Wolfram Alpha.





































